How To Measure BSP Fittings
Post By: Tom Rowse On: 09-03-2020 - Pneumatics
As with all components, pipes and seals for pneumatic systems differ in their specification according to the geographical region in which they're used, and the prevailing industry preferences. The manner of sealing also varies, according to the type of system for which they are designated, and its operating environment. For example, oil and gas applications often use NPT fittings in their pressure systems, while marine applications are more likely to use BSPP adapters.
How To Measure BSP Fittings
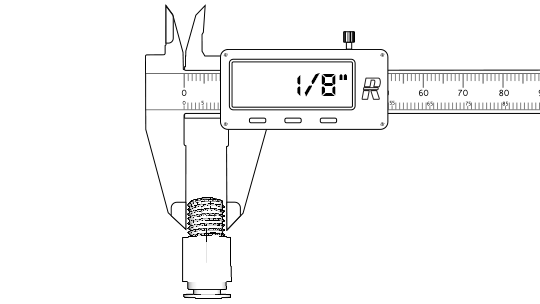
If there is any confusion about which type or size of fitting you have, you'll need to know how to measure your BSP fittings. You can identify any BSPP or BSPT fitting accurately by measuring across the thread from one side to the other. BSPP fittings can be measured more simply, and their specifications can be identified with a few basic calculations.
To determine the thread size:
- Measure the thread's outer diameter (OD) in inches.
- Subtract 25% from the OD measurement.
So if the OD of a BSPP male thread measures one inch (1"), the thread size will be 3/4. In the chart, you'll also see Dash Sizes, which are a convenient shorthand reference for identifying the type. In this example, the thread size would be -12.
The next step is to count the number of threads you have per inch on the fitting to confirm that it is actually a BSP fitting. The easiest way is to count the thread crests over a shorter length, say 1/4", and simply multiply it by 4.
For example, if you count 3.5 thread crests over 1/4":
- 3.5 x 4 = 14 threads per inch.
- Take this measurement and cross-reference it to your thread size in the chart below.
This will match your measurements with the standard BSP sizes and their associated specifications.
Please select an option above.
|
BSPT & BSPP SIZE & PITCH |
DASH SIZE |
BSPT MALE THREAD OD |
BSPP MALE THREAD OD |
BSPT FEMALE THREAD ID |
BSPP FEMALE THREAD ID |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| inch-TPI | mm | inch | mm | inch | mm | inch | mm | inch | |
| 1/8-28 | -02 | 9,5 | 0.37 | 9,6 | 0.38 | 8,4 | 0.33 | 8,6 | 0.34 |
| 1/4-19 | -04 | 12,8 | 0.50 | 13,0 | 0.51 | 11,2 | 0.44 | 11,9 | 0.47 |
| 3/8-19 | -06 | 16,3 | 0.64 | 16,5 | 0.65 | 14,7 | 0.59 | 15,2 | 0.60 |
| 1/2-14 | -08 | 20,4 | 0.80 | 20,8 | 0.82 | 18,3 | 0.72 | 19,1 | 0.75 |
| 5/8-14 | -10 | 22,5 | 0.89 | 22,8 | 0.90 | 20,6 | 0.81 | 20,8 | 0.82 |
| 3/4-14 | -12 | 25,9 | 1.02 | 26,3 | 1.04 | 23,9 | 0.94 | 24,6 | 0.97 |
| 1-11 | -16 | 32,6 | 1.28 | 33,1 | 1.30 | 29,7 | 1.17 | 30,7 | 1.21 |
| 1.1/4-11 | -20 | 41,1 | 1.62 | 41,8 | 1.64 | 38,6 | 1.52 | 39,4 | 1.55 |
| 1.1/2-11 | -24 | 47,0 | 1.85 | 47,7 | 1.88 | 44,5 | 1.75 | 45,5 | 1.79 |
| 2-11 | -32 | 58,6 | 2.31 | 59,5 | 2.34 | 56,4 | 2.22 | 57,4 | 2.26 |
| 2.1/2-11 | -40 | 74,1 | 2.92 | 75,1 | 2.95 | 71,9 | 2.83 | 72,6 | 2.86 |
| 3-11 | -48 | 86,6 | 3.41 | 87,9 | 3.46 | 84,6 | 3.33 | 85,4 | 3.36 |
There is a similar process for determining BSPT sizes, using the same steps to count the threads per inch as in a parallel fitting. However, with a tapered fitting, the OD will obviously change along its length, so this system is not entirely effective. BSPT fittings can be measured instead using the inner diameter. In this instance, a calliper reading can be obtained from inside the fitting bore. The bore size can then be cross-referenced on the chart with the threads per inch and the thread pitch, to determine the standard BSP size and its associated specifications.
National Pipe Thread Fittings
NPT fittings are most commonly found in the United States and Canada. Like all pipe connections there is a male and female joint, and in the NPT seal the male adapter has a tapering thread. The seal is made essentially by force, tightening the male connector into the female until it is pressure-tight, and securing the joint with a sealant. It's not an ideal system, especially with stainless steel joints, which can suffer damage or galling to the threads if the joint is over-tightened or insufficiently lubricated.
British Standard Pipe Fittings
Far more widely used and standardised around the world (except North America) are British Standard Pipe fittings. BSP threads are made in two types of connection, a tapered version (BSPT) like the NPT and a parallel version (BSPP). It's not unusual to confuse the BSPT with the NPT tapered connections, as they are very similar. However, the difference is that NPT threads have a greater angle on the thread flank, at 60°. Both BSPT and BSPP connections have a 55° angle, which can be confirmed using a thread gauge.
BSPP Connections
British Standard Parallel Pipe (BSPP) is the most popular type of connection in the UK and Europe, as well as in South Africa, Australia, New Zealand and Asia. The connector has a parallel thread with, typically, a 30° bevel on the male thread which fits into a 30° cone recessed into the female thread. In some applications, BSPP fittings require a bonded seal washer or O-ring to make the connection.
BSPT Connections
British Standard Pipe Tapered (BSPT) is a tapered thread connection similar to the North American NPT, but distinguished by the 55° flank angle. BSPT pipe sizes generally also have a different thread pitch, but it is sometimes possible to fit an NPT male thread into a BSPT female, and vice versa. Male BSPT fittings can also be threaded into female BSPP fittings, but in either case it's not recommended, as the connections won't form a proper seal. BSPT fittings are sealed by the tapering threads, but will require thread sealant to seal the two parts securely.
Get More From Rowse Straight To Your Inbox